Portable Laser Welding Machines: A Comprehensive Guide
Portable laser welding machines represent a significant advancement in welding technology, offering precision, efficiency, and mobility that traditional welding methods cannot match. These compact devices utilize concentrated laser beams to join metals with minimal heat-affected zones, making them increasingly popular across industries from automotive repair to jewelry making. As technology advances, these portable units are becoming more accessible to both professionals and hobbyists.
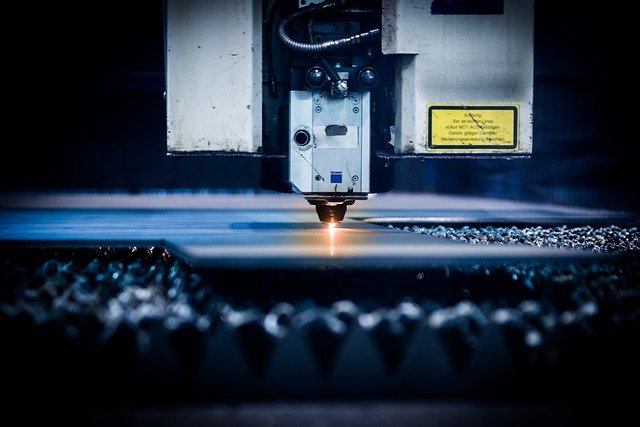

Portable laser welding machines combine a compact fiber laser source with a handheld welding head, enabling fast, clean joins on metals with minimal distortion. They pack industrial capability into a mobile footprint, often on a small cart with an integrated chiller, controller, and safety features. For many teams, the appeal is consistent quality, reduced post-processing, and flexibility for on-site fabrication and repair.
What Are Portable Laser Welding Machines?
Portable laser welding machines are handheld or cart-mounted systems that focus a high-intensity laser beam to fuse metals along a seam. Most models use fiber lasers in the 1000–2000 W range, a wobble head for wider seams, and optional wire feeders for filling gaps. They excel on thin to medium-gauge stainless steel, carbon steel, and aluminum, and can be configured for copper or brass with appropriate settings and operator skill. Compared with TIG or MIG, these units localize heat, often producing narrower heat-affected zones, tighter control, and visually clean welds that need less grinding or polishing.
Benefits and Applications of Portable Laser Welding
The main benefits include speed, consistency, and finish. In many scenarios, operators report faster travel speeds than TIG for comparable joints, with reduced distortion and fewer cosmetic defects that would otherwise require rework. The resulting lower heat input helps maintain material properties and keeps adjacent surfaces cleaner. Typical applications include stainless steel enclosures, HVAC and ducting, automotive bodywork repair, furniture frames, signage, food-processing equipment, and on-site maintenance where moving a large assembly to a fixed cell is impractical. Many devices also offer quick-change nozzles for cleaning or surface preparation, increasing utility without adding bulk.
How to Find Portable Laser Welding Machines
Start with clear requirements: material types, joint geometry, maximum thickness, and desired finish quality. Compare specifications such as laser power, beam quality, wobble frequency and amplitude ranges, compatible filler wire diameters, and duty cycle. Verify safety interlocks, dual-trigger controls, and availability of proper eyewear rated for the laser wavelength. Assess ergonomics of the handpiece, cable length, and the stability of the cooling system. Review service options, availability of spare parts and consumables (nozzles, protective lenses), and training resources. Ask for application samples or live demos, and review documented parameter libraries for your alloys to reduce commissioning time.
Where to Buy Portable Laser Welding Machines
You can purchase from manufacturers directly, authorized distributors, and industrial equipment resellers. Trade shows and regional demonstrations help you validate performance and compare models side by side. If you need short-term capacity, some distributors and integrators offer rentals or pilot programs in your area. Ensure the provider can support installation, operator training, and safety compliance. Look for documented warranty terms, response times for service, and clear return or upgrade options. Reliable after-sales support can be as important as the machine’s headline specifications.
Cost Considerations for Portable Laser Welding Machines
Total cost involves more than the purchase price. Key drivers include laser power (e.g., 1000 vs. 2000 W), brand and laser source, wobble head capabilities, wire feeder inclusion, and the quality of the chiller. Accessories such as safety eyewear, fume extraction, and gas supply add to the budget, as do shipping, import duties, commissioning, and operator training. Ongoing costs include shielding gas, contact tips/nozzles, protective windows for the lens, and periodic maintenance of the cooling system. The table below provides real-world example ranges to illustrate the market landscape; actual quotes vary by configuration and region.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| LightWELD 1500/2000 handheld laser welder | IPG Photonics | USD 18,000–30,000 |
| Handheld Fiber Laser Welding Machine 1500W | Han’s Laser | USD 9,000–18,000 |
| Handheld Fiber Laser Welder 1500W | Herolaser | USD 6,000–12,000 |
| HWS Handheld Laser Welder 1500–2000W | HSG Laser | USD 10,000–20,000 |
| Handheld Fiber Laser Welding Machine 1000–2000W | LXSHOW | USD 5,500–10,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Beyond purchase price, consider productivity impacts. Faster travel speeds and reduced finishing can offset capital expenditure over time, especially for repetitive stainless assemblies. Factor in training duration to reach stable quality, and include safety infrastructure—proper laser eyewear, interlocks, warning signage, and fume extraction—when comparing options. If you plan to weld aluminum regularly, confirm pulse or wobble settings and the availability of compatible filler wire to achieve consistent penetration and cosmetic quality.
A brief checklist can help during evaluations: request sample welds on your exact materials and thicknesses; document parameter settings used; confirm availability of local services for installation and repairs; and verify spare parts lead times. Ask for written warranty terms and calibration procedures, and ensure power and cooling requirements match your facility.
In summary, portable laser welding machines offer a compact path to high-quality metal joining with less distortion and rework compared to many conventional processes. By aligning power, features, and support with your materials and workload—and by validating costs using multiple quotes—you can integrate a system that improves throughput and finish quality in a wide range of fabrication and maintenance tasks.